- Sodium [Na] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses.
- Sodium
- History of Sodium
- How to Locate Sodium on Periodic Table
- Sodium Facts
- Sodium Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
- Ground State Electronic Configuration of Sodium - neutral Sodium atom
- Atomic Spectrum of Sodium
- Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
- Sodium Chemical Properties : Sodium Ionization Energies and electron affinity
- Use of Sodium
Sodium [Na] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses.

Sodium
Sodium is the 11th element of Periodic table with atomic number 11, atomic weight 22.98977. S Symbol Na, has a Body Centered Cubic structure and Silver color. Sodium is a alkali metal element. Trivial name of Sodium is alkali metals. Know everything about Sodium Facts, Physical Properties, Chemical Properties, Electronic configuration, Atomic and Crystal Structure.

History of Sodium
The element Sodium was discovered by Humphry Davy in year 1807 in United Kingdom. Sodium derived its name from the English word soda (natrium in Latin)
Sodium /ˈsoʊdiəm/ is a chemical element with symbol Na (from Ancient Greek Νάτριο) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silver-white, highly reactive metal. In the Periodic table it is in column 1 (alkali metals), and shares with the other six elements in that column that it has a single electron in its outer shell, which it readily donates, creating a positively charged atom – a cation.
How to Locate Sodium on Periodic Table
Periodic table is arranged by atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus which is same as number of electrons. The atomic number increases from left to right. Periodic table starts at top left ( Atomic number 1) and ends at bottom right (atomic number 118). Therefore you can directly look for atomic number 11 to find Sodium on periodic table.
Another way to read periodic table and locate an element is by using group number (column) and period number (row). To locate Sodium on periodic table look for cross section of group 1 and period 3 in the modern periodic table.
Sodium Facts
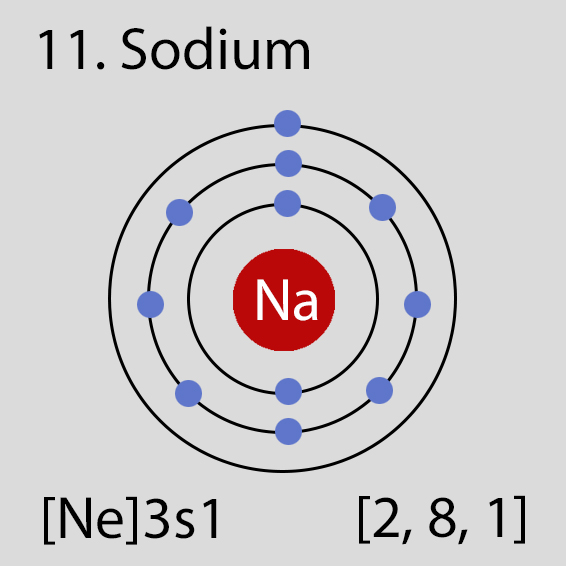
Sodium Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
Sodium atoms have 11 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 8, 1] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 2S1/2.
Element Properties
Atomic Structure of Sodium
Ground State Electronic Configuration of Sodium - neutral Sodium atom
The ground state electronic configuration of Neutral Sodium atom is [Ne] 3s1. The portion of Sodium configuration that is equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, is abbreviated as [Ne]. For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used.This is important as it is the Valence electrons 3s1, electrons in the outermost shell that determine the chemical properties of the element.
Unabbreviated electronic configuration of neutral Sodium
Complete ground state electronic configuration for the Sodium atom, Unabbreviated electronic configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
Atomic Spectrum of Sodium

Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
Sodium Chemical Properties : Sodium Ionization Energies and electron affinity
Use of Sodium
Sodium is used as a heat exchanger in some nuclear reactors, and as a reagent in the chemicals industry. But sodium salts have more uses than the metal itself. The most common compound of sodium is sodium chloride (Nacl). It is added to food and used to de-ice.