- Nitrogen [N] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses
- Nitrogen
- History of Nitrogen
- How to Locate Nitrogen on Periodic Table
- Nitrogen Facts
- Nitrogen Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
- Ground State Electronic Configuration of Nitrogen - neutral Nitrogen atom
- Atomic Spectrum of Nitrogen
- Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
- Nitrogen Chemical Properties: Nitrogen Ionization Energies and electron affinity
- Use of Nitrogen
Nitrogen [N] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses

Nitrogen
Element 7 of Periodic table is Nitrogen with atomic number 7, atomic weight 14.0067. Nitrogen, symbol N, has a Simple Hexagonal structure and Colorless color. Nitrogen is a other nonmetal element. Trivial name of Nitrogen is pentels, pnictogens*. Know everything about Nitrogen Facts, Physical Properties, Chemical Properties, Electronic configuration, Atomic and Crystal Structure.

History of Nitrogen
The element Nitrogen was discovered by Daniel Rutherford in year 1772 in United Kingdom . Nitrogen derived its name from the Greek word nitron and ‘-gen’ meaning ‘niter-forming’
Nitrogen is a chemical element with symbol N and atomic number 7. It is the lightest pnictogen and at room temperature, it is a transparent, odorless diatomic gas. Nitrogen is a common element in the universe, estimated at about seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System.
How to Locate Nitrogen on Periodic Table
Periodic table is arranged by atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus which is same as number of electrons. The atomic number increases from left to right. Periodic table starts at top left ( Atomic number 1) and ends at bottom right (atomic number 118). Therefore you can directly look for atomic number 7 to find Nitrogen on periodic table.
Another way to read periodic table and locate an element is by using group number (column) and period number (row). To locate Nitrogen on periodic table look for cross section of group 15 and period 2 in the modern periodic table.
Nitrogen Facts
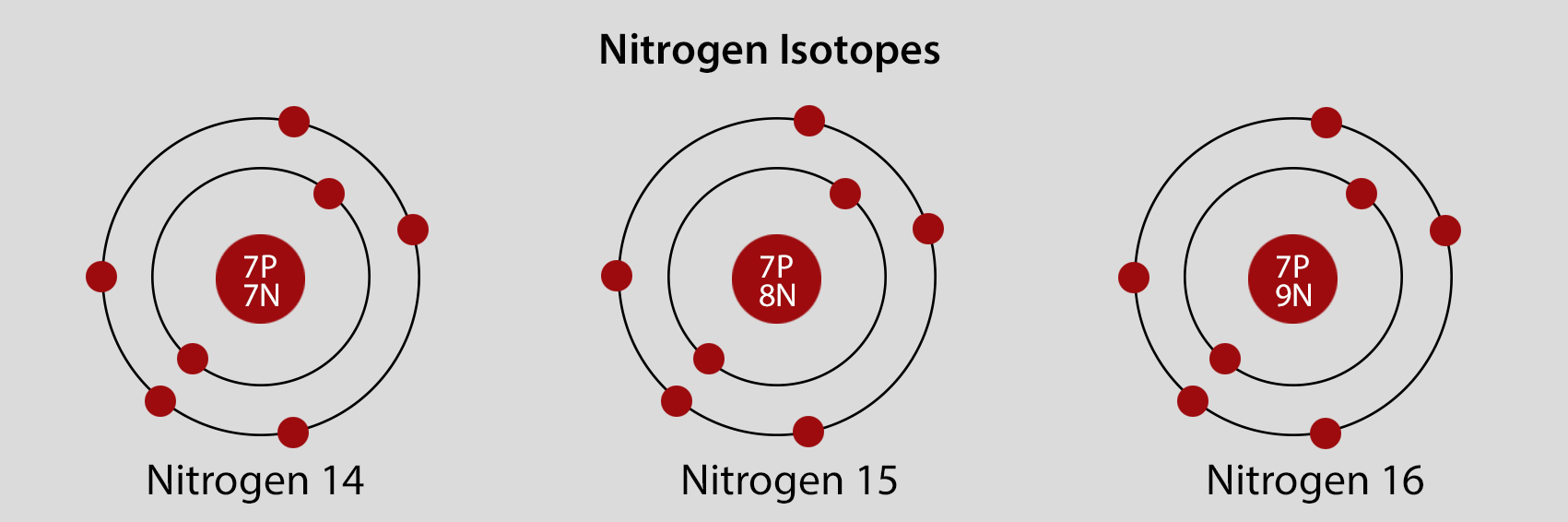
Nitrogen Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
Nitrogen atoms have 7 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 5] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 4S3/2.

Element Properties
Atomic Structure of Nitrogen
Ground State Electronic Configuration of Nitrogen - neutral Nitrogen atom
The ground state electronic configuration of Neutral Nitrogen atom is [He] 2s2 2p3. The portion of Nitrogen configuration that is equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, is abbreviated as [He]. For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used.This is important as it is the Valence electrons 2s2 2p3, electrons in the outermost shell that determine the chemical properties of the element.
Unabbreviated electronic configuration of neutral Nitrogen
Complete ground state electronic configuration for the Nitrogen atom, Unabbreviated electronic configuration
1s2 2s2 2p3
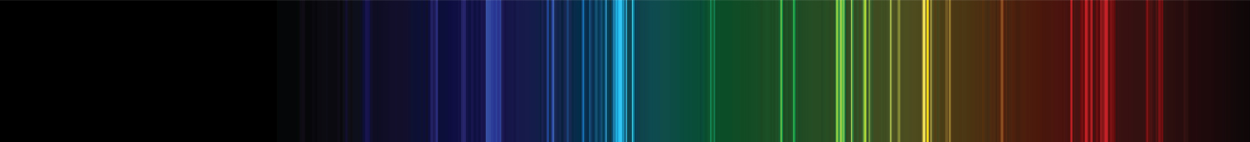
Atomic Spectrum of Nitrogen
Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
Nitrogen Chemical Properties: Nitrogen Ionization Energies and electron affinity
Use of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is very useful to the chemical industry. It is used to produce Fertilizers, Nitric acid, Nylon, Dyes and Explosives. To make these products, nitrogen must first be reacted with hydrogen to produce ammonia.