- Fluorine [F] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses
- Fluorine
- History of Fluorine
- How to Locate Fluorine on Periodic Table
- Fluorine Facts
- Fluorine Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
- Ground State Electronic Configuration of Fluorine - neutral Fluorine atom
- Atomic Spectrum of Fluorine
- Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
- Fluorine Chemical Properties :Fluorine Ionization Energies and electron affinity
- Use of Fluorine
Fluorine [F] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses

Fluorine
Element 9 of Periodic table is Fluorine with atomic number 9, atomic weight 18.9984032. Fluorine, symbol F, has a Base Centered Monoclinic structure and Colorless color. Fluorine is a halogens element. Trivial name of Fluorine is halogens*. Know everything about Fluorine Facts, Physical Properties, Chemical Properties, Electronic configuration, Atomic and Crystal Structure.

History of Fluorine
The element Fluorine was discovered by André-Marie Ampère in year 1886 in France . Fluorine derived its name from the Latin fluere, meaning ‘to flow’
Fluorine is a chemical element with symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists as a highly toxic pale yellow diatomic gas at standard conditions. As the most electronegative element, it is extremely reactive:almost all other elements, including some noble gases, form compounds with fluorine.
How to Locate Fluorine on Periodic Table
Periodic table is arranged by atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus which is same as number of electrons. The atomic number increases from left to right. Periodic table starts at top left ( Atomic number 1) and ends at bottom right (atomic number 118). Therefore you can directly look for atomic number 9 to find Fluorine on periodic table.
Another way to read periodic table and locate an element is by using group number (column) and period number (row). To locate Fluorine on periodic table look for cross section of group 17 and period 2 in the modern periodic table.
Fluorine Facts
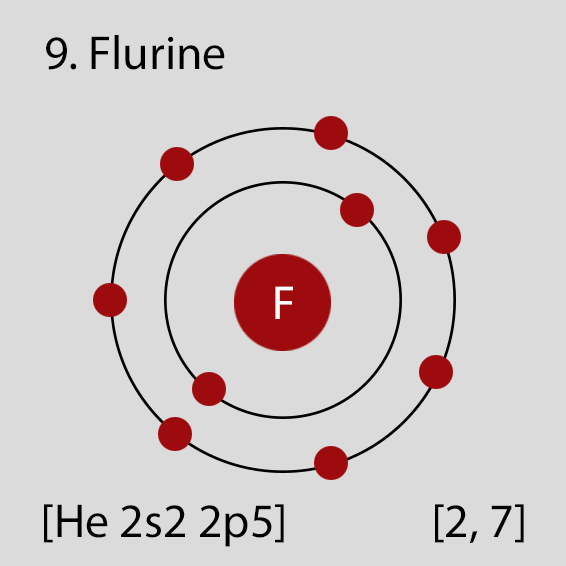
Fluorine Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
Fluorine atoms have 9 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 7] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 2P3/2.
Element Properties
4S3/2
Atomic Structure of Fluorine
Ground State Electronic Configuration of Fluorine - neutral Fluorine atom
The ground state electronic configuration of Neutral Fluorine atom is [He] 2s2 2p5. The portion of Fluorine configuration that is equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, is abbreviated as [He]. For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used.This is important as it is the Valence electrons 2s2 2p5, electrons in the outermost shell that determine the chemical properties of the element.
Unabbreviated electronic configuration of neutral Fluorine
Complete ground state electronic configuration for the Fluorine atom, Unabbreviated electronic configuration
1s2 2s2 2p5
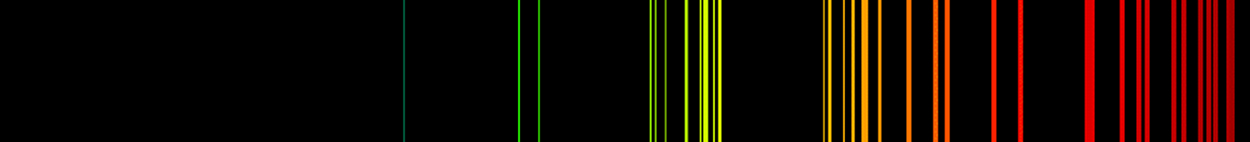
Atomic Spectrum of Fluorine
Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
Fluorine Chemical Properties :Fluorine Ionization Energies and electron affinity
Use of Fluorine
What are the uses of fluorine? Fluorine is critical for the production of nuclear material for nuclear power plants and for the insulation of electric towers. Hydrogen fluoride, a compound of fluorine, is used to etch glass. Fluorine, like Teflon, is used to make plastics and is also important in dental health