- Sulfur [S] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses.
- Sulfur
- History of Sulfur
- How to Locate Sulfur on Periodic Table
- Sulfur Facts
- Sulfur Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
- Element Properties
- Atomic Structure of Sulfur
- Crystal Structure of Sulfur
- Ground State Electronic Configuration of Sulfur- neutral Sulfur atom
- Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
- Sulfur Chemical Properties : Sulfur Ionization Energies and electron affinity
- Sulfur Physical & Elastic Properties
- Sulfur Electrical Properties
- Sulfur Magnetic Properties
- Sulfur Thermal Properties
- Use of Sulfur
Sulfur [S] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses.

Sulfur
Sulfur is 16th element of Periodic table with atomic number 16, atomic weight 32.065. Sulfur, symbol ‘S’, has a Simple Triclinic structure and Colorless color. Sulfur is a other nonmetal element. Trivial name of Sulfur is pentels, pnictogens*. Know everything about Sulfur Facts, Physical Properties, Chemical Properties, Electronic configuration, Atomic and Crystal Structure.

History of Sulfur
The element Sulfur was discovered in year 500 BC by Ancient china in unknown place . Sulfur derived its name from the Latin word sulphur, ‘fire and brimstone.
Sulfur is a chemical element with symbol ‘S’ and atomic number 16. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8.
How to Locate Sulfur on Periodic Table
Periodic table is arranged by atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus which is same as number of electrons. The atomic number increases from left to right. Periodic table starts at top left ( Atomic number 1) and ends at bottom right (atomic number 118). Therefore you can directly look for atomic number 16 to find Sulfur on periodic table.
Another way to read periodic table and locate an element is by using group number (column) and period number (row). To locate Sulfur on periodic table look for cross section of group 16 and period 3 in the modern periodic table
Sulfur Facts
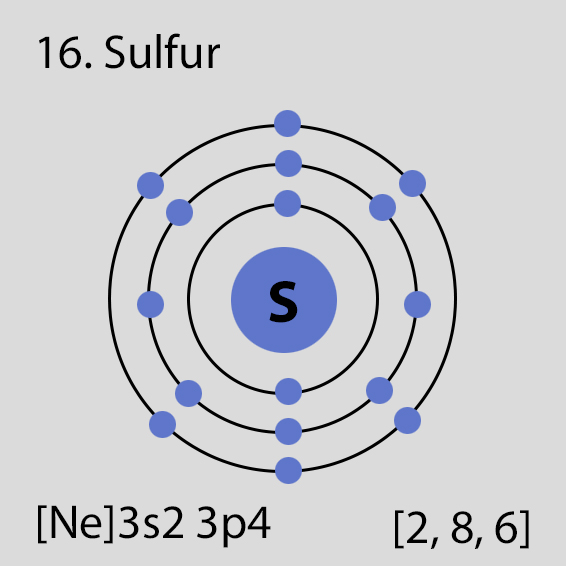
Sulfur Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
Sulfur atoms have 16 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 8, 6] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 3P2.

Element Properties
3P2
Atomic Structure of Sulfur
Crystal Structure of Sulfur
The solid state structure of Sulfur is Face Centered Orthorhombic.
The Crystal structure can be described in terms of its unit Cell. The unit Cells repeats itself in three dimensional space to form the structure.
The unit cell is represented in terms of its lattice parameters, which are the lengths of the cell edges Lattice Constants (a[1043.7], b[1284.5] and c[2436.9 pm]) and the angles between them Lattice Angles (alpha[π/2], beta[π/2] and gamma[π/2])
The positions of the atoms inside the unit cell are described by the set of atomic positions ( xi, yi, zi) measured from a reference lattice point.
The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space are described by the 230 space groups (219 distinct types, or 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct
Space Group Name
Space Group Number
Crystal Structure
Fddd
70
Face Centered Orthorhombic
Ground State Electronic Configuration of Sulfur- neutral Sulfur atom
The ground state electronic configuration of Neutral Sulfur atom is [Ne] 3s2 3p4. The portion of Sulfur configuration that is equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, is abbreviated as [Ne]. For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used.This is important as it is the Valence electrons 3s2 3p4, electrons in the outermost shell that determine the chemical properties of the element.
Unabbreviated electronic configuration of neutral Sulfur
Complete ground state electronic configuration for the Sulfur atom, Unabbreviated electronic configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
Sulfur Chemical Properties : Sulfur Ionization Energies and electron affinity
Sulfur Physical & Elastic Properties
Sulfur Electrical Properties
Sulfur Magnetic Properties
Sulfur Thermal Properties
Use of Sulfur
The normal forms of Sulfur is yellow crystals or powder. Sulfur is used in the vulcanisation of black rubber, as a fungicide and in black gunpowder. Most sulfur is used in the production of sulfuric acid, which is perhaps the most important chemical.