- Potassium
- History of Potassium
- How to Locate Potassium on Periodic Table
- Potassium Facts
- Potassium Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
- Element Properties
- Atomic Structure of Potassium
- Crystal Structure of Potassium
- Ground State Electronic Configuration of Potassium- neutral potassium atom
- Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
- Potassium Physical Properties
- Potassium Elastic Properties
- Potassium Electrical Properties
- Potassium Magnetic Properties
- Potassium Thermal Properties
- Use of Potassium
Potassium [K] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses.
Potassium
Potassium is 19th element of Periodic table with atomic number 19, atomic weight 39.0983. Symbol ‘K’, has a Body Centered Cubic structure and Silver color. Potassium is a Alkali Metal element. It is part of group 1 (lithium family). Know everything about Potassium Facts, Physical Properties, Chemical Properties, Electronic configuration, Atomic and Crystal Structure.
History of Potassium
The element Potassium was discovered by H. Davy in year 1807 in United Kingdom. Potassium was first isolated by H. Davy in 1807. Potassium derived its name from New Latin potassa, ‘potash’ (kalium in Latin).
Davy discovered it by using electrolysis on potash.
How to Locate Potassium on Periodic Table
Periodic table is arranged by atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus which is same as number of electrons. The atomic number increases from left to right. Periodic table starts at top left ( Atomic number 1) and ends at bottom right (atomic number 118). Therefore you can directly look for atomic number 19 to find Potassium on periodic table.
Another way to read periodic table and locate an element is by using group number (column) and period number (row). To locate Potassium on periodic table look for cross section of group 1 and period 4 in the modern periodic table.
Potassium Facts
Potassium Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
Potassium atoms have 19 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 8, 8, 1] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 1S1/2.
Element Properties
Atomic Structure of Potassium
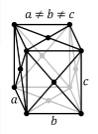
Crystal Structure of Potassium
The solid state structure of Potassium is Body Centered Cubic.
The Crystal structure can be described in terms of its unit Cell. The unit Cells repeats itself in three dimensional space to form the structure.
Unit Cell Parameters
The unit cell is represented in terms of its lattice parameters, which are the lengths of the cell edges Lattice Constants (a, b and c).
The unit cell is represented in terms of its lattice parameters, which are the lengths of the cell edges Lattice Constants (a[532.8 pm], b[525.6 pm] and c[532.8 pm]) and the angles between them Lattice Angles (alpha[π/2], beta[π/2] and gamma[π/2])
The positions of the atoms inside the unit cell are described by the set of atomic positions ( xi, yi, zi) measured from a reference lattice point.
The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space are described by the 230 space groups (219 distinct types, or 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct.
Crystal Structure
Number of atoms per unit cell
229
Body Centered Cubic
2
Ground State Electronic Configuration of Potassium- neutral potassium atom
Abbreviated electronic configuration of Potassium
The ground state abbreviated electronic configuration of Neutral Potassium atom is [Ar] 4s1. The portion of Potassium configuration that is equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, is abbreviated as [Ar]. For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used. This is important as it is the Valence electrons 4s1, electrons in the outermost shell that determine the chemical properties of the element.
Unabbreviated electronic configuration of neutral Potassium
Complete ground state electronic configuration for the Potassium atom, Unabbreviated electronic configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1
Electrons are filled in atomic orbitals as per the order determined by the Aufbau principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule.
- As per the Aufbau principle the electrons will occupy the orbitals having lower energies before occupying higher energy orbitals. According to this principle, electrons are filled in the following order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p…
- The Pauli exclusion principle states that a maximum of two electrons, each having opposite spins, can fit in an orbital.
- Hund’s rule states that every orbital in a given subshell is singly occupied by electrons before a second electron is filled in an orbital.
Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
Potassium Physical Properties
Potassium Elastic Properties
Potassium Electrical Properties
Potassium Magnetic Properties
Potassium Thermal Properties
Use of Potassium
Potassium plays an important role in the transmission of nerve signals, muscle contractions, fluid balance, and various chemical reactions. Potassium is most commonly used for treating and preventing low potassium levels, treating high blood pressure, and preventing stroke.