- Magnesium [Mg] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses.
- Magnesium
- History of Magnesium
- How to Locate Magnesium on Periodic Table
- Magnesium Facts
- Magnesium Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
- Element Properties
- Atomic Structure of Magnesium
- Ground State Electronic Configuration of Magnesium - neutral Magnesium atom
- Atomic Spectrum of Magnesium
- Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
- Magnesium Chemical Properties : Magnesium Ionization Energies and electron affinity
- Use of Magnesium
Magnesium [Mg] – Element Details, History, Atomic Structure, Facts, Properties, Electronic Configuration, Atomic Spectrum, Uses.

Magnesium
Magnesium is the 12th Element of Periodic table with atomic number 12, atomic weight 24.305. , symbol Mg, has a Simple Hexagonal structure and Silver color. Magnesium is a alkaline earth metal element. Trivial name of Magnesium is alkaline earth metals*. Know everything about Magnesium Facts, Physical Properties, Chemical Properties, Electronic configuration, Atomic and Crystal Structure.

History of Magnesium
The element Magnesium was discovered by Joseph Black in year 1755 in United Kingdom . Magnesium derived its name from Magnesia, a district of Eastern Thessaly in Greece
Magnesium is a chemical element with symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray solid which bears a close physical resemblance to the other five elements in the second column (Group 2, or alkaline earth metals) of the periodic table:they each have the same electron configuration in their outer electron shell producing a similar crystal structure. Magnesium is the ninth most abundant element in the universe.
How to Locate Magnesium on Periodic Table
Periodic table is arranged by atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus which is same as number of electrons. The atomic number increases from left to right. Periodic table starts at top left ( Atomic number 1) and ends at bottom right (atomic number 118). Therefore you can directly look for atomic number 12 to find Magnesium on periodic table.
Another way to read periodic table and locate an element is by using group number (column) and period number (row). To locate Magnesium on periodic table look for cross section of group 2 and period 3 in the modern periodic table.
Magnesium Facts
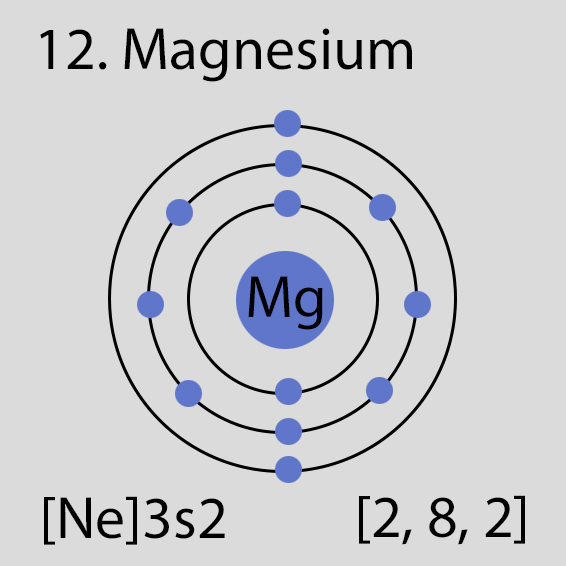
Magnesium Atomic Structure and Orbital Properties
Magnesium atoms have 12 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 8, 2] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 1S0

Element Properties
1S0
Atomic Structure of Magnesium
Ground State Electronic Configuration of Magnesium - neutral Magnesium atom
The ground state electronic configuration of Neutral Magnesium atom is [Ne] 3s2. The portion of Magnesium configuration that is equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, is abbreviated as [Ne]. For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used.This is important as it is the Valence electrons 3s2, electrons in the outermost shell that determine the chemical properties of the element.
Unabbreviated electronic configuration of neutral Magnesium
Complete ground state electronic configuration for the Magnesium atom, Unabbreviated electronic configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
Atomic Spectrum of Magnesium

Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
Magnesium Chemical Properties : Magnesium Ionization Energies and electron affinity
Use of Magnesium
Magnesium is used as a cofactor in more than 300 enzyme systems that regulate diverse biochemical reactions in the body, including protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and blood pressure regulation. Magnesium is required for energy production, oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis.